比较关注硬件的应该都用过 GPU-Z 这个软件,可以查看显卡的所有硬件信息和传感器数据。
在 Sensors 标签里应该可以看到 Hot Spot 温度,这个究竟是指什么呢?

起源
Hot Spot 这个概念最初由 AMD 创造,在农企的卡上这个参数叫 Junction Temperature ,而这个温度的读数却要比核心温度还要高一些,这是因为什么呢。
当初 5700 系列发售的时候,AMD 官方在论坛发了以下内容:
Junction Temperature: Enhanced Thermal Monitoring
In the past, the GPU core temperature was read by a single sensor that was placed in the vicinity of the legacy thermal diode. This singular sensor was used to make all power-performance optimization decisions across the entire GPU. However, depending on the game being run, the type of GPU cooling and other related metrics, different parts of the GPU might have been at different levels of utilization. As a result, ramping up or throttling down the entire GPU based on this single measurement was inefficient, often leaving significant thermal headroom – and resulting performance – on the table.
With the AMD Radeon VII GPU we introduced enhanced thermal monitoring to further optimize GPU performance. We built upon that foundation with the Radeon RX 5700 series GPUs, and now utilize an extensive network of thermal sensors distributed across the entire GPU die to intelligently monitor and tune performance in response to granular GPU activity in real time.
Paired with this array of sensors is the ability to identify the ‘hotspot’ across the GPU die. Instead of setting a conservative, ‘worst case’ throttling temperature for the entire die, the Radeon RX 5700 series GPUs will continue to opportunistically and aggressively ramp clocks until any one of the many available sensors hits the ‘hotspot’ or ‘Junction’ temperature of 110 degrees Celsius. Operating at up to 110C Junction Temperature during typical gaming usage is expected and within spec. This enables the Radeon RX 5700 series GPUs to offer much higher performance and clocks out of the box, while maintaining acoustic and reliability targets.
We provide users with both measurements – the average GPU Temperature and Junction Temperature – so that they have the best and most complete visibility into the operation of their Radeon RX 5700 series GPUs.
如何理解这段话呢?
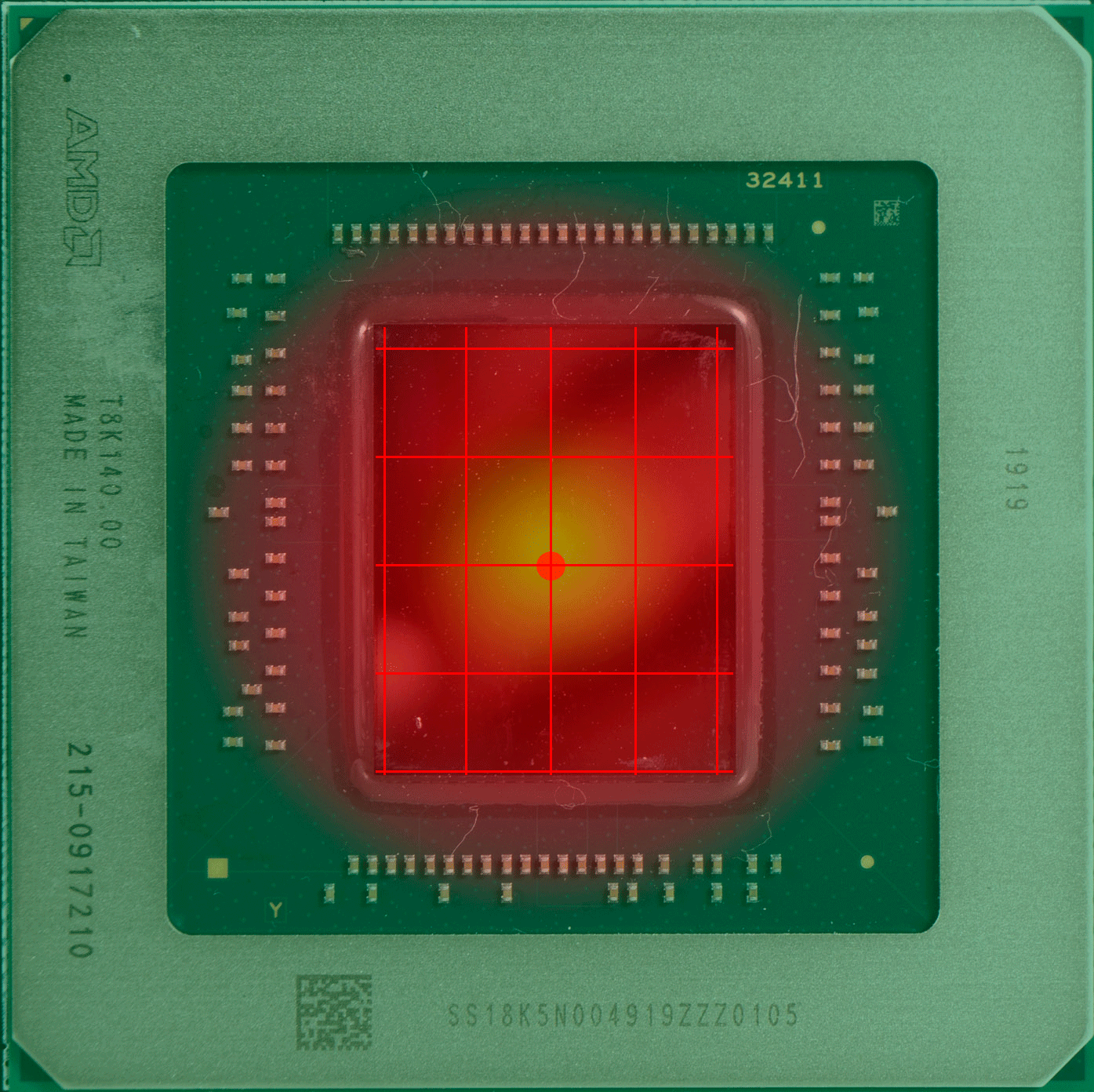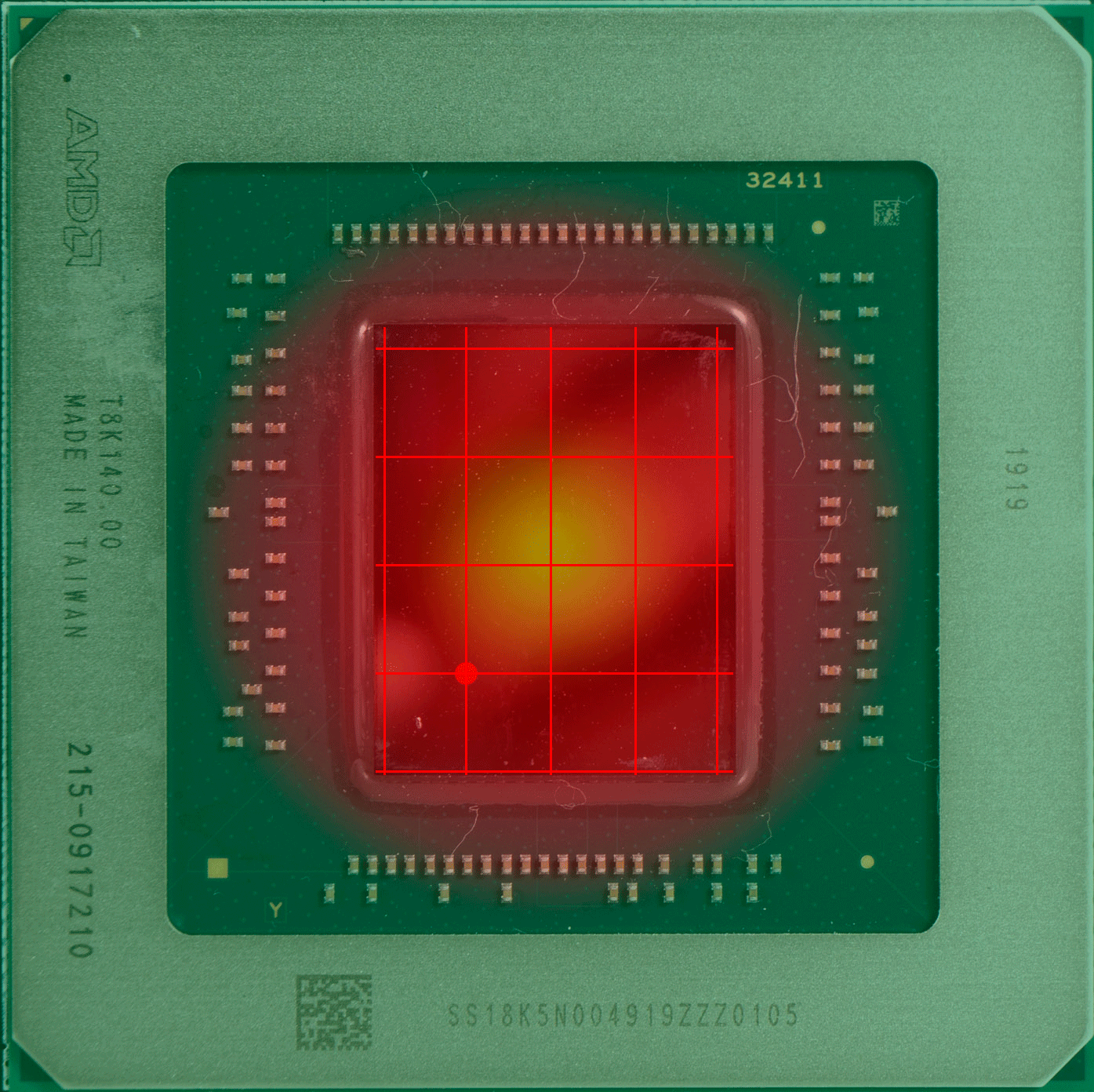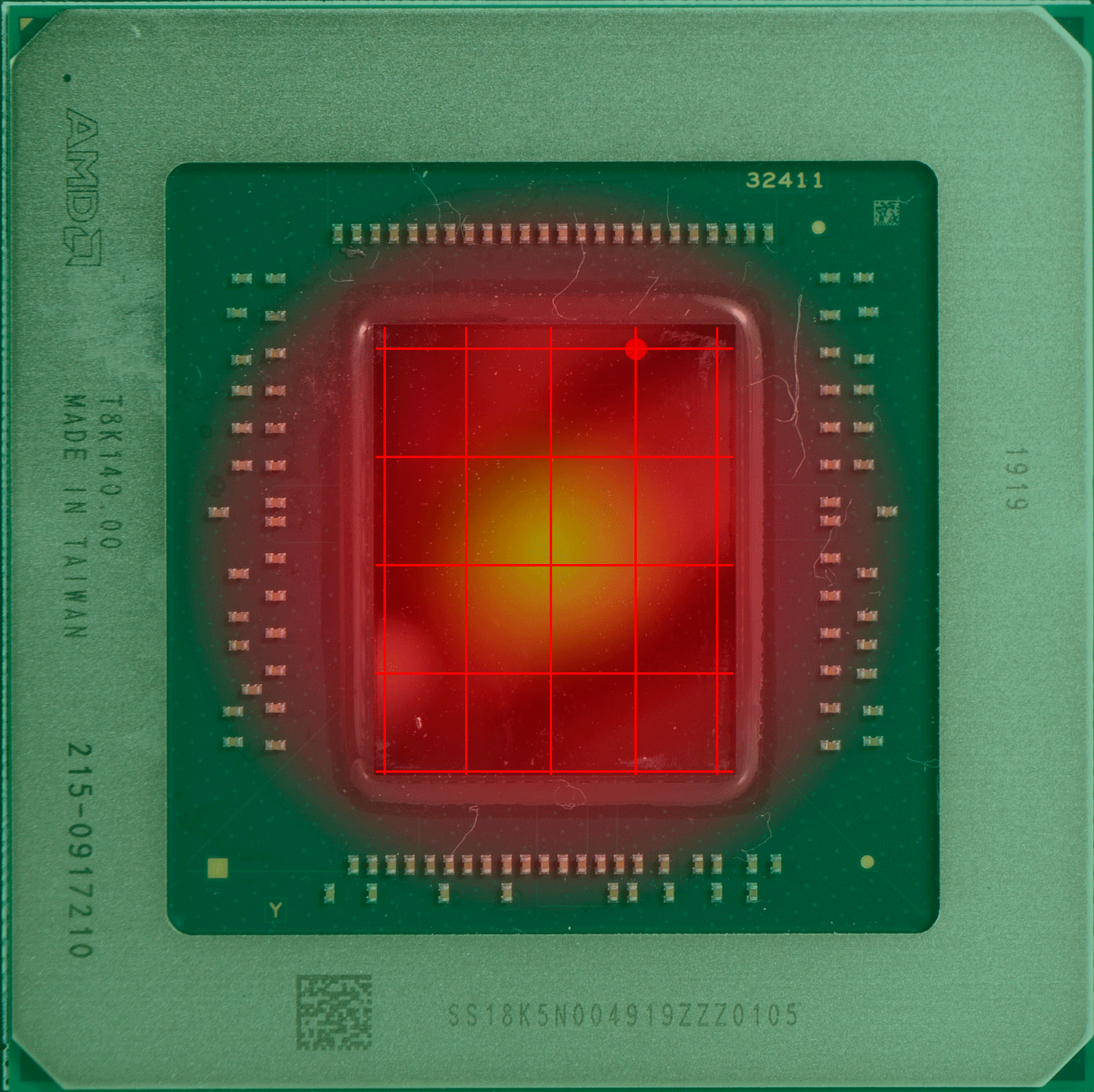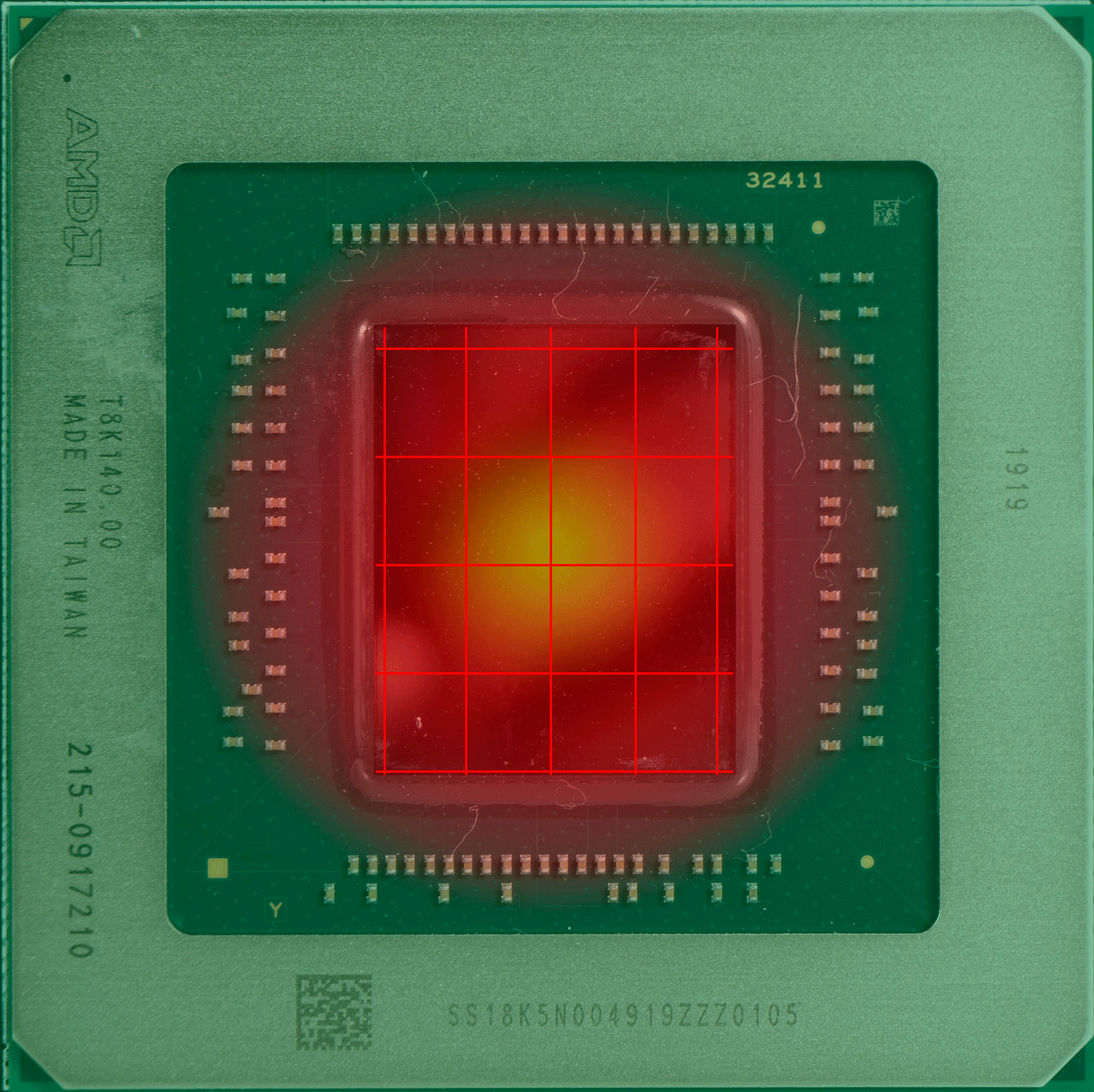
其实很简单,Sensors 中的核心温度的读数一般来自内置在核心中的传感器而来,而传感器只有一个,且位置固定,一般在核心的中间区域附近。
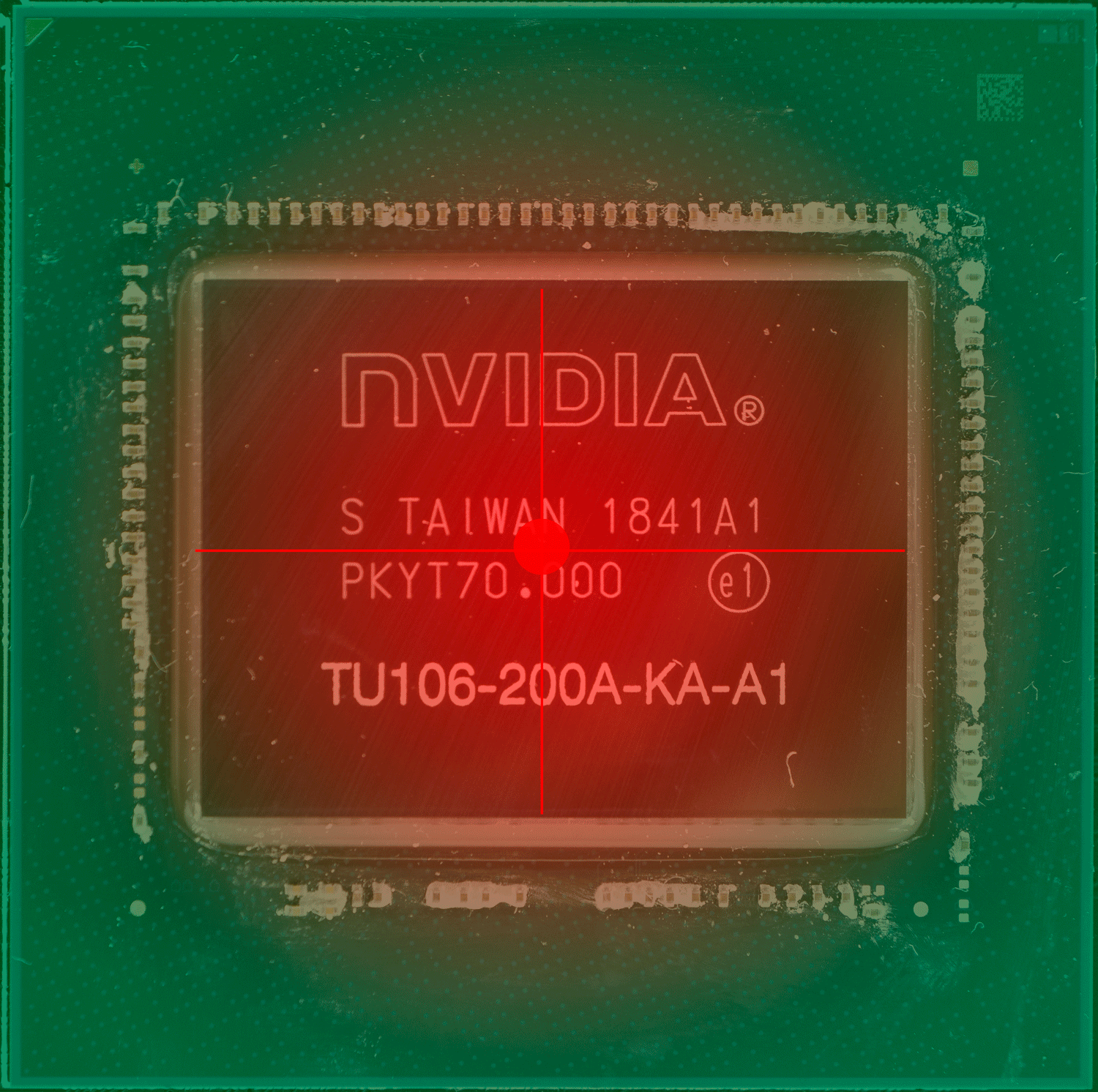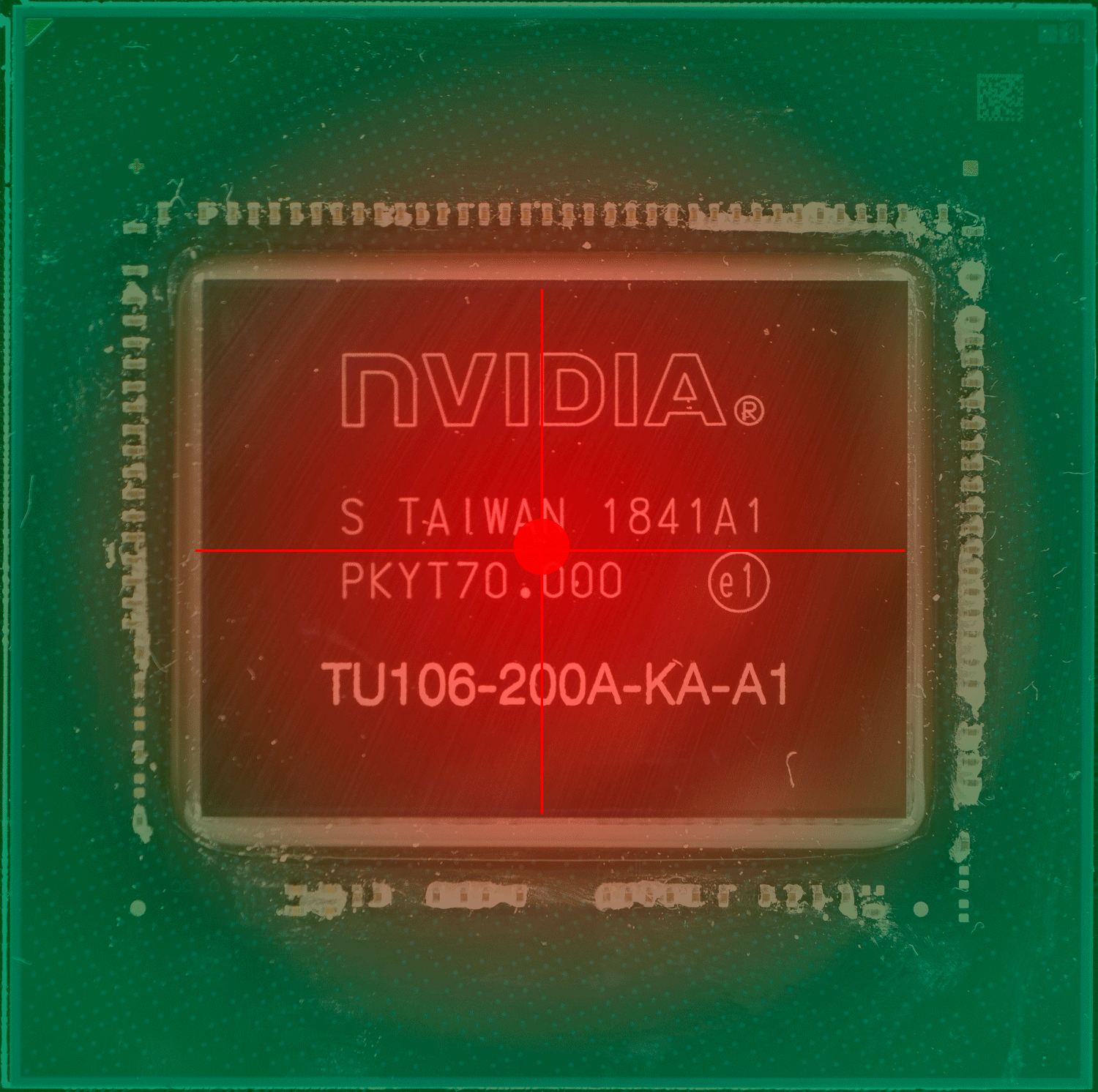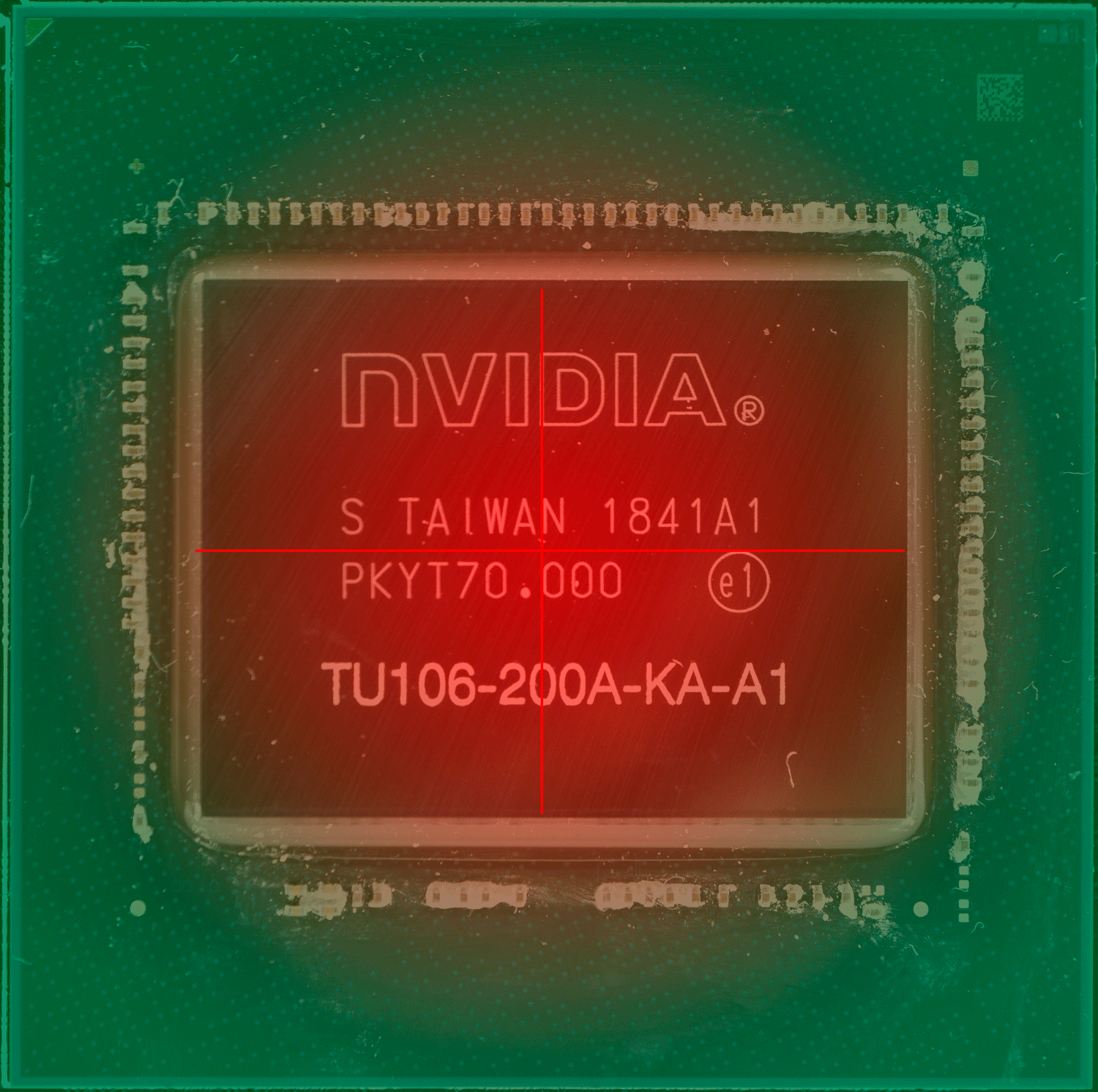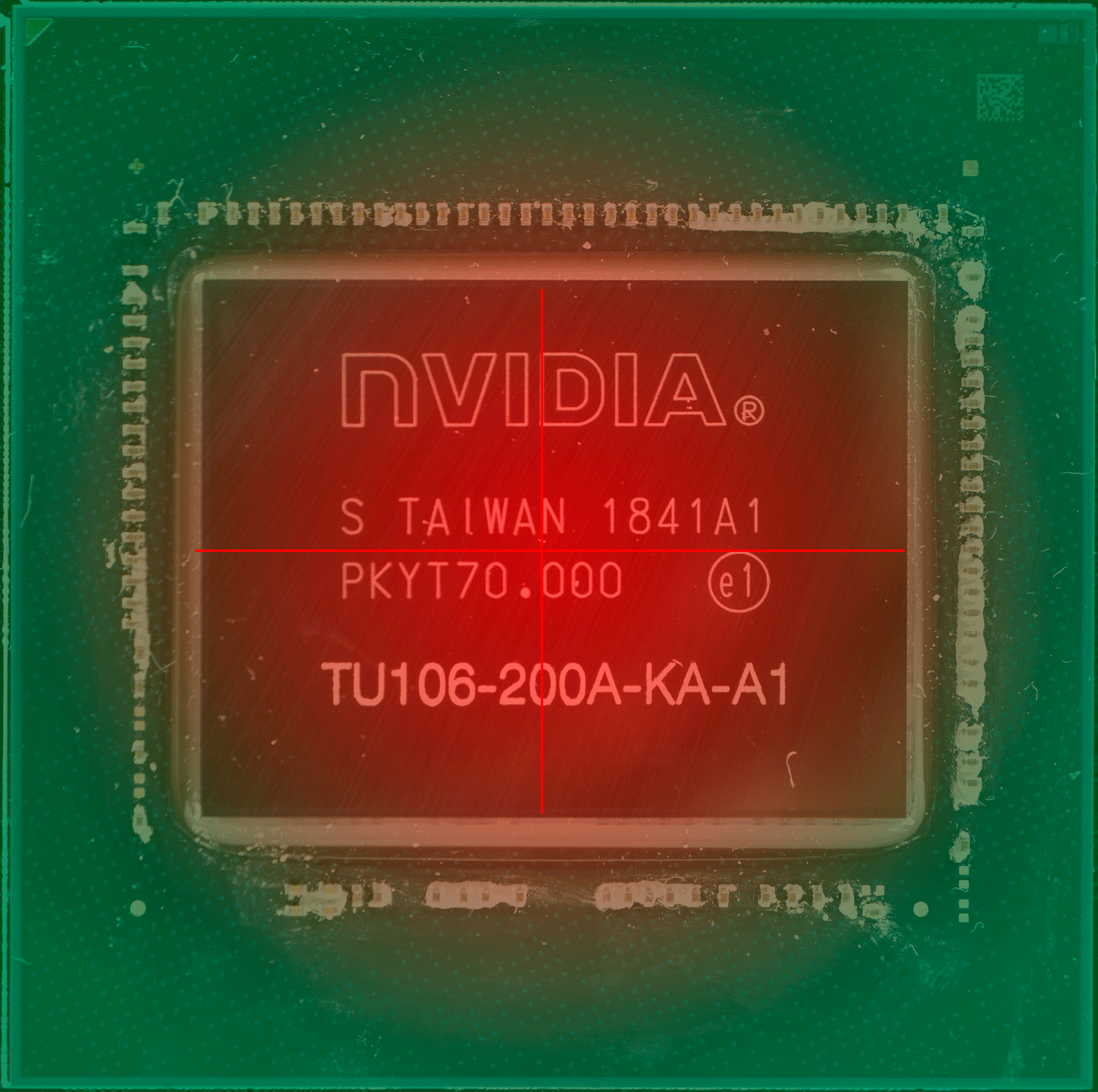
上图中的红点,就是传感器的“假定点”(因为超微半导体和英伟达并未公布过传感器的实际位置)核心温度的读数会直接影响 GPU 的加速频率和风扇等策略,但实际上 GPU 的设计和 CPU 一样,是分区域的,不同的区域有不同的逻辑电路,导致不同的区域也有不同功能,不同的功能就导致不同的负载,也就导致不同区的温度也不同,因此某个点的温度并不能代表其他区域的温度。
具体哪个区域的温度高,这通常取决于核心正在做的事情更多用到哪部分的单元,哪部分就更热一些。而固定位置的测量需要留下一定的余量,避免核心其他位置出现远超出测量点的温度,例如英伟达 RTX 系列显卡的核心温度上限就是83度,当核心温度达到83度的时候,加速频率机制就会停止。
关于核心分区这块可以找找英特尔的芯片分析或者参考非常复杂的 CPU 电路图是如何做出来的? - 郑培柱的回答 - 知乎。

改进
AMD 认为以这种单一测量方式来对 GPU 进行加速或限制频率的方式是低效的,实际上 GPU 仍有余力进行更高性能的频率加速。所以在 RX 5700 系列上,AMD 为 Navi 10 核心设计了一系列的温度传感器,这些传感器分布在核心的不同位置,而 Junction Temperature 并不是某一个点的温度,而是轮询所有的传感器,其中最高温度的那个点会成为 Junction Temperature 的读数,可以理解为显卡的“焦点温度”。
换句话说,这种策略下并不需要为核心温度保留余量空间,更多的温度传感器能测量 GPU 不同位置的温度,同时这些位置只要有任何一个地方达到上限就会停止频率加速,这种测量方式可以保证 GPU 整体处在更安全的温度范围,同时让 GPU 拥有更精确加速频率的机制。
附录
参考链接
- NVIDIA GPUs Have Hotspot Temperature Sensors Like AMD - Techpowerup
- RX 5700/RX 5700 XT高达100度的Hot Spot到底是什么? - 哔哩哔哩
本文由 柒 创作,采用 知识共享署名4.0
国际许可协议进行许可。
转载本站文章前请注明出处,文章作者保留所有权限。
最后编辑时间: 2025-07-31 02:00 AM
